Power Path software solution enables generation of multiple reports, such as SAG-tension report, support report, quantity report and power line coordinates report.
In this post we will explain each part of Quantity report.
The report can be exported in .txt or .xslx file.
Follow the numbers for an explanation:

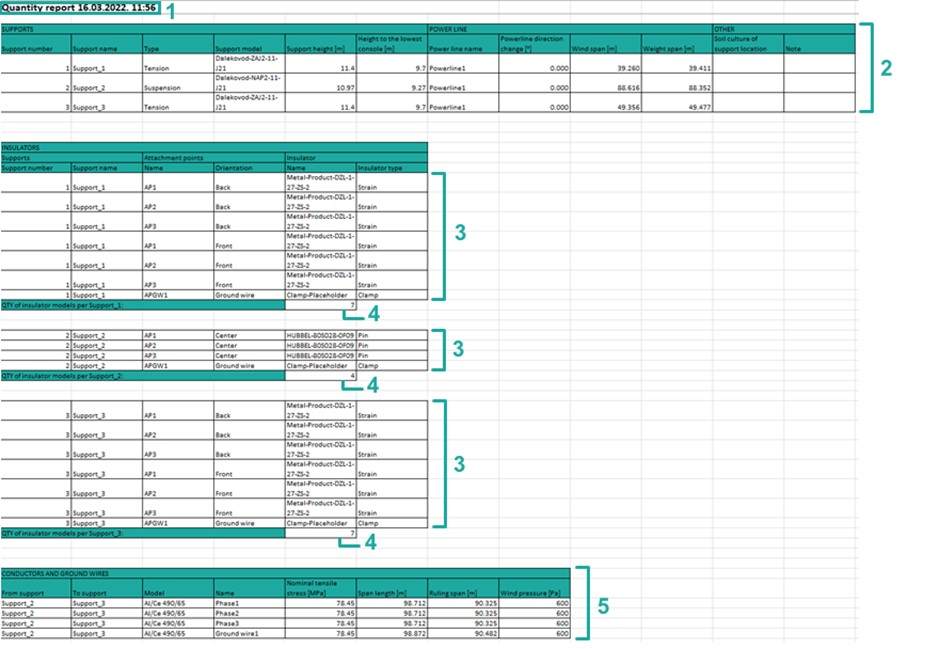
1. Basic report information such as report type, the data and time when report was made.
2. Table of basic information about supports, power lines and other:
2.1 Support number – the number of the support in the power line.
2.2 Support name – name of the support. It is the name that the user enters when adding a support (Add Support).
2.3 Type – type of the support. Type can be tension and suspension (Add Support).
2.4 Support model – model of the support (Add Support).
2.5 Support height – height of the support (Add Support Data).
2.6 Height to the lowest console – height from the ground to the lowest console of the support.
2.7 Power line name – name of the powerline (Draw Power Line).
2.8 Power line direction change – value of angle between previous and forward power line direction according to the referent tension support expressed in [0C].
2.9 Wind span – half of the sum of adjacent spans (distance from half of one catenary to the half of the adjacent catenary).
2.10 Weight span – distance from the lowest point of one catenary to the lowest point of adjacent catenary.
2.11 Soil culture of support location – where you can write what kind of soil is where power line is designed.
2.12 Note – where you can write notes.
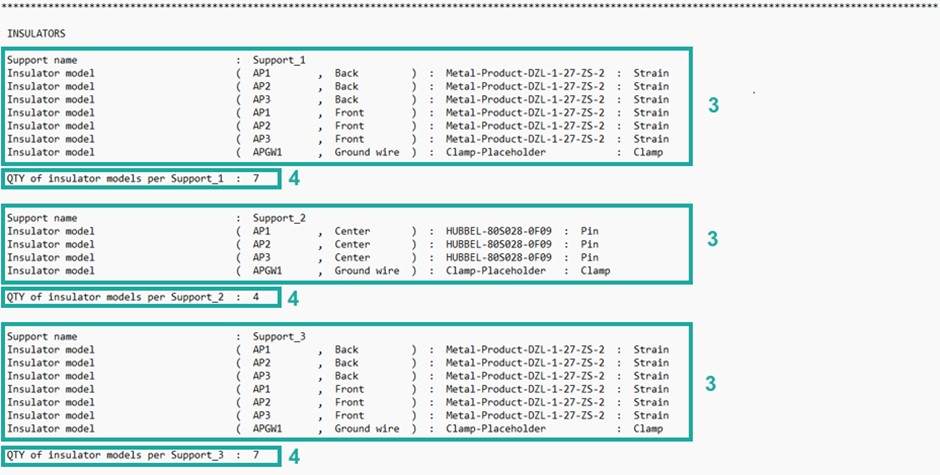
3. Table of basic information about insulators:
3.1 Support where the attachment point is set:
3.1.1. Support number – the number of the support in the power line.
3.1.2 Support name – name of the support. It is the name that the user enters when adding a support (Add Support).
3.2 Attachment point on support where the insulator is set:
3.2.1. Name – name of attachment point (Add Support Data).
3.2.2 Orientation – front or back side of support (Add Support Data).
3.3 Insulator set on attachment point:
3.3.1. Name – name of the insulator (Add Insulator).
3.3.2 Insulator Type – type of the insulator (Add Insulator Data).
4. Number of the insulator models per support.
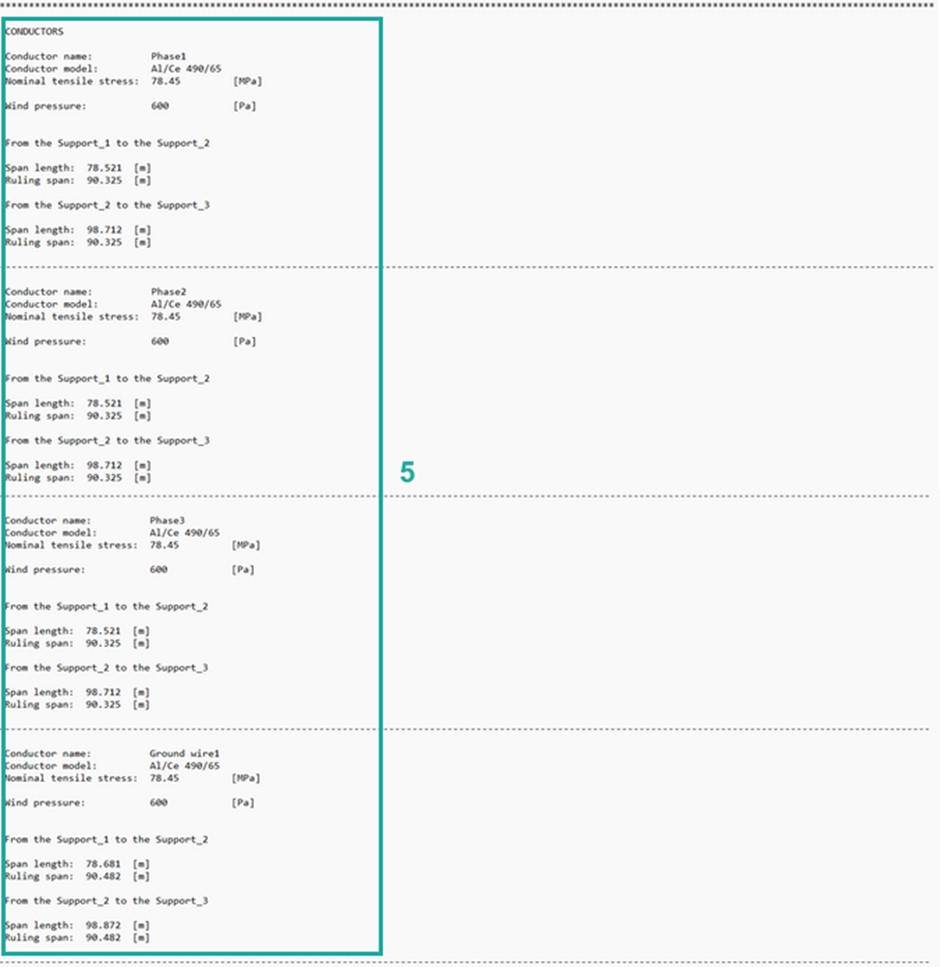
5. Table of basic information about conductors and ground wires:
5.1 From support and To support – names of the supports between where the conductor is attached.
5.2 Model – model of the conductor. Name of the conductor that indicates what it is made of or from which manufacturer is produced (Add Conductor Data).
5.3 Name – name of the conductor. It is the name that the user enters when adding a conductor on power line (Add Conductor).
5.4 Nominal tensile stress – normal permissible conductor stress expressed in [MPa]. Mechanical conductor parameter (Add Conductor Data).
5.5 Span length – the shortest horizontal distance between two supports.
5.6 Ruling span – equivalent span or mean effective span, is an assumed uniform design span. Ruling span is used to determine tensile stress.
5.7 Wind pressure – pressure of wind expressed in [Pa]. The wind pressure is defined in Weather Conditions, and it is additional load on conductor (Add Weather Conditions).
If you want to learn how to generate Quantity report, visit our knowledge base – Create Quantity report
If you want immediately to start creating your own OHL project with the BIM approach, import your data, and use the solution for any 2D drafting and 3D modeling in technical projects, try a 30 days trial of Power Path.
